Outline
① 운영체제 Definition
② 컴퓨터 시스템 Organization
③ 컴퓨터 시스템 Architecture
④ 운영체제 Structure
⑤ 운영체제 Operation
① 운영체제 Definition
● 운영체제 역할
1. 컴퓨터 하드웨어 관리
2. 프로그램 실행 제어
-> 운영체제 그 자체로는 유용한 기능 못함.
-> 다른 프로그램이 유용한 작업을 할 수 있는 환경 제공

● 운영체제 위치
응용 프로그램과 컴퓨터 하드웨어 사이
● 운영체제 목표
1. 사용자 프로그램 실행 및 사용자 문제 해결 용이하도록
2. 컴퓨터 시스템 사용 편리하게
3. 컴퓨터 하드웨어 효율적인 방법으로 사용하도록
● 운영체제
1. resource allocator
- 효율적이고 공평한 자원 사용을 위해 자원을 어떻게 할당할 지 결정
2. control program
- 에러와 부적절한 컴퓨터 시스템의 사용을 방지하기 위해 프로그램 실행을 제어
② 컴퓨터 시스템 Organization
● 4가지 기본 원리
1. Computer system I/O operation
2. I/O structure
3. Interrupt
4. Storage structure
+ Multi-processor systems
1. Computer system I/O operation
I/O: 메모리 <-> 로컬 버퍼 간 데이터 이동
I/O device와 CPU가 동시에 작업 수행
인터럽트를 발생시킴으로써 Device controller가 CPU에게 I/O 연산이 끝났다는 것을 알려줌
2. I/O structure
Bus
A bus is a collection of parallel wires that carry address, data, and control signals.

DMA (Direct Memory Access)
CPU의 간섭 없이 I/O Device <-> 메모리 간 데이터 송수신
I/O Device가 전송 작업을 수행하고 있는 동안 CPU는 다른 작업 수행 가능
3. Interrupt
Operating System -> Interrupt driven (수많은 interrupt가 지속적으로 발생)
Program Counter: 다음에 실행될 명령어의 주소 저장

1) Interrupt: 프로세서 외부에서 발생 (Hardware)
- Ctrl + C
2) Trap: instruction 실행의 결과로 발생하는 이벤트에 의해 발생 (Software)
- System call, Segmentation fault, exception
소프트웨어 에러 또는 요청 -> exception, trap 생성
- div by 0, request for operating system service
4. Storage structure
1) Main memory
2) Secondary storage
Caching is an important principle of computer systems
③ 컴퓨터 시스템 Architecture
● Multiprocessors
장점
1. throughput 증가
2. 경제적
3. 신뢰성 증가
※ 오버헤드 때문에 성능 n배 보다 작음
④ 운영체제 structure
● Multiprogramming
CPU와 I/O device 동시에 작업 수행하도록 유지
Job scheduling에 의해 진행됨
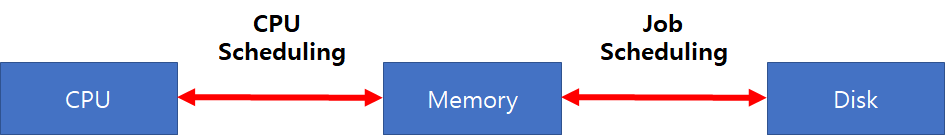
CPU Scheduling
- If several jobs ready to run at the same time
Job Scheduling
- If several jobs are ready to be brought into memory, and there is not enough room for them
Swapping
- If processes don't fit in memory, swapping moves them in and out to run
Virtual memory
- allows execution of processes that are not completely in memory
- Virtual memory (CPU가 보는 주소) > Physical Memory (실제 공간)
⑤ 운영체제 operation
Dual mode
1. user mode
2. kernel mode (previleged mode)
-> mode bit 사용
-> OS 보호하기 위해서
previleged instruction
-> 커널 모드에서만 실행됨
-> 사용자 모드에서 실행할 경우 trap 발생
-> trap, interrupt 발생 시 사용자 모드에서 커널 모드로 전환됨
'CS 공부 > 운영체제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter 6, 7 Process Synchronization (0) | 2021.09.23 |
|---|---|
| Chapter 5. Process scheduling (0) | 2021.09.23 |
| Chapter 4. Threads & Concurrency (0) | 2021.09.17 |
| Chapter 3. Process Concept (0) | 2021.09.16 |
| Chapter 2 (0) | 2021.09.16 |